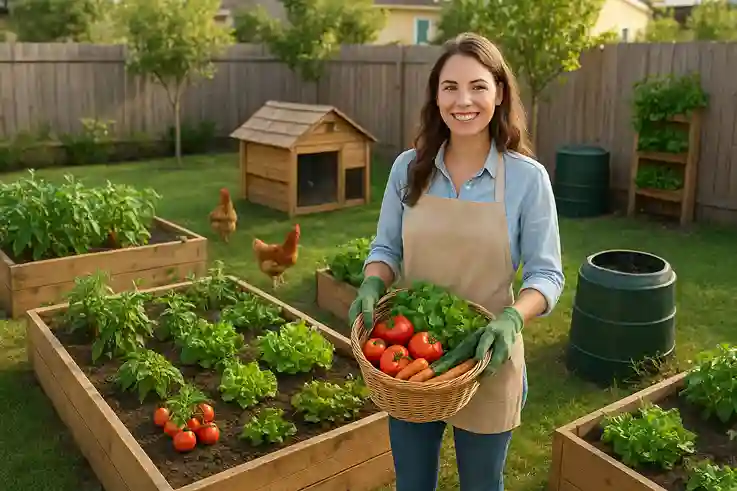
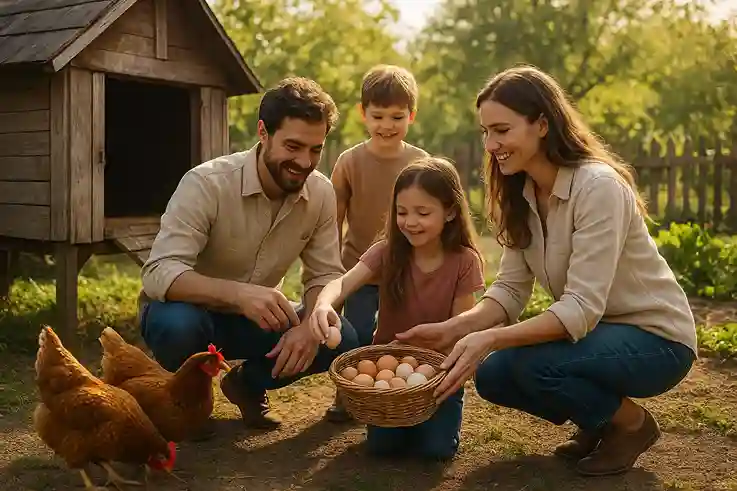
Profitable Backyard Farm
A backyard farm is becoming an increasingly popular choice in the United States as grocery prices rise, sustainable living gains attention, and more people seek self-sufficiency. Many are realizing that growing their own food is not only a fulfilling hobby but also a smart way to save money and achieve greater independence.
But what if your love for gardening and fresh produce could also become a profitable venture? With the right planning and approach, a backyard farm can generate income — whether as a part-time side hustle or a full-time small business.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn exactly how to start a profitable backyard farm in America. From suburban backyards to rural plots and even city spaces with limited room, we’ll cover everything you need to transform your patch of land into a productive, money-making backyard farm.
Now is the perfect time to take your passion for growing food to the next level with backyard farming that’s both sustainable and profitable.
What Is a Backyard Farm?
A backyard farm is a small-scale agricultural setup right on your residential property. It can involve growing vegetables, raising chickens or bees, cultivating herbs, or even selling compost.
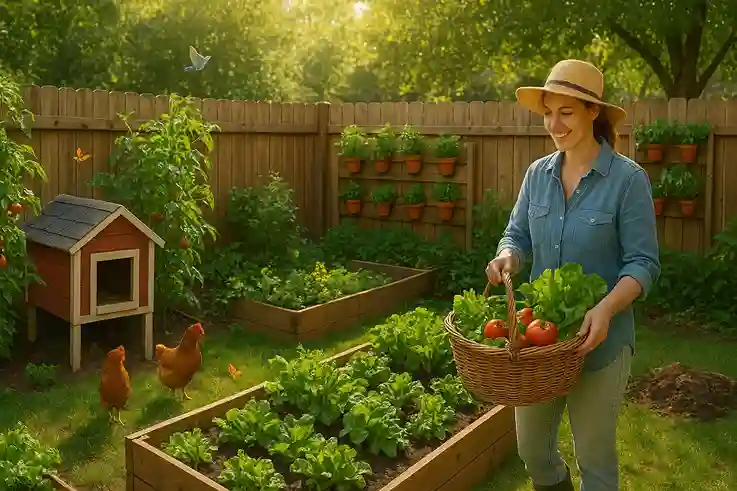

Low-Cost, Sustainable, and Scalable
Minimal Upfront Investment
Starting a backyard farm doesn’t require large sums of money. Basic tools, seeds, and a few containers or raised beds are often enough to get started. You can begin small, test what works in your space, and reinvest profits as your farm grows. This low-cost approach makes backyard farming accessible to nearly anyone.
Eco-Friendly Practices
Backyard farming encourages sustainable living. Composting kitchen scraps, collecting rainwater, and using organic methods reduce waste and minimize environmental impact. Growing your own food also lowers your carbon footprint by cutting down on store-bought produce transportation.
Scalable Growth
A backyard farm can expand gradually to match your goals. Start with a few vegetable beds or a small flock of chickens. Over time, you can add more crops, bees, or even a small greenhouse. This flexibility ensures your farm grows with your ambition without overwhelming your resources or space.
No Acres Needed — Small Spaces Can Thrive
You don’t need acres of land to start a successful backyard farm. Even a small suburban yard, a rooftop, or a city balcony can produce vegetables, herbs, and small livestock with the right setup. Container gardening, vertical planters, and raised beds make the most of limited space while keeping crops accessible and manageable.
Planning is Key
Careful planning is essential for a productive backyard farm. Start by mapping your space, deciding which crops or animals suit your climate, and creating a planting or rotation schedule. Efficient layouts and proper crop selection ensure maximum yield from minimal space.
Consistent Effort Pays Off
A modest backyard requires regular attention to reach its full potential. Watering, weeding, fertilizing, and monitoring plant or animal health are small daily tasks that add up. With consistent care, even a compact space can become a profitable and sustainable backyard farm.
Purpose-Driven Farming
Knowing why you’re farming helps maintain focus and motivation. Whether your goal is fresh produce, supplemental income, or eco-friendly living, having a clear purpose guides your decisions and makes your backyard farming journey more rewarding.
Why Start a Backyard Farm in 2025?
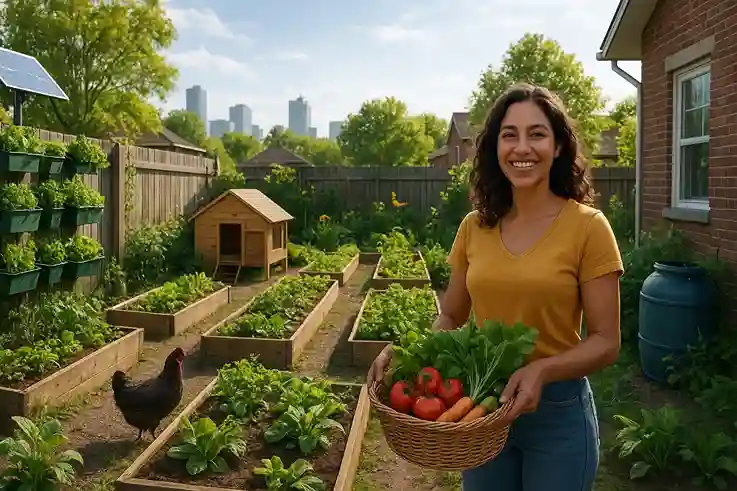

Food Prices Are High
With grocery prices steadily increasing, many Americans are looking for practical ways to reduce food costs. A backyard farm allows households to grow their own vegetables, fruits, and herbs, cutting reliance on store-bought produce. Over time, this can significantly lower monthly grocery bills while providing fresh, high-quality food.
Sustainability Matters
Embracing Local and Organic Produce
Today’s consumers are more conscious about the origin and quality of their food. Fresh, local, and organic produce is highly sought after. A backyard farm lets you grow your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs, ensuring top quality and nutrition while reducing reliance on store-bought options.
Eco-Friendly Practices at Home
Backyard farming naturally supports sustainability. Homegrown food reduces transportation emissions, packaging waste, and dependence on industrial agriculture. Practices like composting, rainwater collection, and natural pest control make your farm both productive and environmentally responsible.
Aligning with Market Trends
Homegrown produce isn’t just sustainable—it’s trendy. Many consumers prefer organic and local foods, and growing your own aligns perfectly with these market shifts. By cultivating a backyard farm, you contribute to the broader movement toward eco-conscious and health-focused living.
Benefits Beyond the Environment
Sustainability through backyard farming also strengthens personal and community connections. Sharing fresh produce, teaching others about eco-friendly gardening, or simply enjoying the process of growing your own food adds value far beyond financial savings.
Direct-to-Consumer Is Thriving
Backyard farming offers a unique opportunity to sell directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels. Farmers can market fresh produce, eggs, honey, or herbs through farmers’ markets, online platforms, or CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) programs. This direct connection with customers not only builds trust and loyalty but also allows backyard farmers to capture higher profits while sharing the value of homegrown, sustainable food.
Government & State Incentives
Starting a backyard farm is becoming more accessible thanks to a growing number of government and state programs designed to support local food production. Many states offer grants, low-interest loans, and training programs that provide essential knowledge for urban agriculture and small-scale farming. Workshops, online resources, and mentorship programs help backyard farmers learn best practices for soil management, crop rotation, and sustainable techniques.
These incentives make backyard farming more feasible, reduce startup risks, and empower both beginners and experienced growers to expand their operations and maximize productivity while contributing to the local food system.
Step-by-Step: How to Start a Profitable Backyard Farm
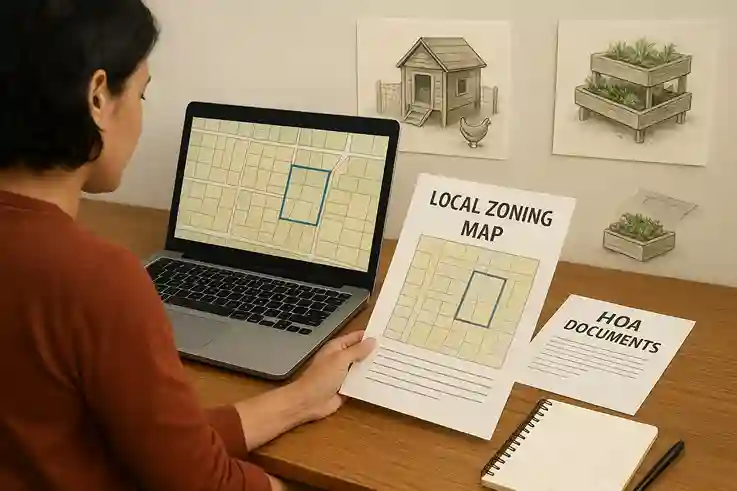
1. Assess Your Space and Local Laws
Before you plant a single seed:
Measure Your Space
Before starting a backyard farm, it’s essential to evaluate the space you have. Consider garden beds, patios, balconies, and even vertical spaces like fences, walls, or trellises. Understanding your yard’s full potential helps you make informed decisions about what to grow or raise.
Plan According to Dimensions
Accurately measuring your available area allows for efficient layout planning. Knowing the exact dimensions helps determine how many vegetable beds, herb containers, or small livestock enclosures your backyard farm can accommodate. It also ensures proper spacing for sunlight, irrigation, and air circulation, which are crucial for healthy growth.
Maximize Small Spaces
Even limited areas can be productive with creative solutions. Vertical gardening, raised beds, container planting, and tiered setups allow you to maximize yield without needing acres of land. Measuring and planning your space carefully lays the foundation for a successful and profitable backyard farm.
Check Zoning Laws and HOA Rules
Before starting your backyard farm, it’s important to review local zoning laws. Different municipalities may have rules regarding the types of crops you can grow, raising livestock, or selling your produce. Being aware of these regulations helps you avoid fines or forced removal of your farm structures.
Review HOA Guidelines
If you live in a community governed by a homeowners association (HOA), check their rules carefully. Some HOAs restrict livestock, limit the number of garden structures, or have specific requirements for aesthetics. Understanding these guidelines ensures your backyard farming activities remain compliant.
Plan Within Legal Limits
By checking zoning laws and HOA rules in advance, you can design your farm layout and choose crops or animals that fit legal requirements. This planning prevents future headaches and ensures your backyard farm can operate smoothly, whether for personal use or profit.
Confirm Access to Sunlight, Water, and Drainage
Sunlight Is Key
For a productive backyard farm, sunlight is essential. Most vegetables, herbs, and fruiting plants need at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Observe your space throughout the day to identify shaded areas and choose the best spots for sun-loving crops.
Easy Access to Water
Reliable water access is another critical factor. Whether using a hose, rain barrel, or irrigation system, your backyard farming setup should allow for consistent watering without much hassle. Proper hydration keeps plants healthy and supports optimal growth and yield.
Ensure Proper Drainage
Good drainage prevents water from pooling around plant roots, which can cause rot or disease. Assess soil type and consider raised beds or well-draining containers if your yard tends to retain water. Planning for drainage ensures your backyard farm thrives even during heavy rain.
Plan for Optimal Growth
By confirming sunlight, water, and drainage, you create the ideal conditions for your crops or small livestock. Thoughtful placement of beds, containers, or enclosures maximizes productivity and ensures your backyard farm remains sustainable and profitable.
💡 Tip: Even a 500–1,000 sq ft garden can generate solid income with intensive growing methods.
2. Choose a Profitable Niche
Think beyond just veggies. Your backyard farm can be specialized for higher profits:
| Niche | High-Profit Ideas |
|---|---|
| Vegetables | Heirloom tomatoes, salad greens, peppers |
| Herbs | Basil, mint, lavender, medicinal herbs |
| Livestock | Chickens (eggs), rabbits, quail |
| Specialty | Mushrooms, microgreens, edible flowers |
| Products | Homemade soaps, hot sauces, canned goods |
🎯 Focus on what grows well in your zone and what people are willing to buy.
3. Start Small, Scale Smart
When starting a backyard farm, it’s best to start small. Focus on crops or animals you can easily manage while learning the basics of backyard farming. Starting modestly reduces stress, limits risk, and allows you to gain hands-on experience before expanding.
Suggested Starter Projects
Raised Garden Beds or Vertical Farming
Raised garden beds and vertical farming is ideal for small-space backyard farming. They allow you to maximize limited areas while improving soil quality and drainage. Raised beds reduce soil compaction, keep weeds under control, and make harvesting easier. Vertical planters, trellises, or wall-mounted systems help you grow climbing vegetables, herbs, or greens without taking up valuable ground space. Both methods increase yield per square foot and make your backyard farm more organized, productive, and visually appealing.
Small Chicken Coop
A small chicken coop is a great way to add livestock to your backyard farm without taking up too much space. Raising a few hens can provide a steady supply of fresh eggs, reduce grocery costs, and even create natural fertilizer for your garden. Before building or purchasing a coop, always check local city ordinances and HOA rules, as some neighborhoods have restrictions on livestock. Proper planning ensures your chickens thrive while keeping your farm compliant and harmonious with neighbors.
One or Two Types of Produce
Starting with just one or two types of crops helps you manage your backyard farm efficiently while testing what grows best in your space and climate. Focus on produce that is easy to cultivate, fast-growing, and in demand—like tomatoes, lettuce, or herbs. This approach lets you learn planting, watering, and harvesting techniques without feeling overwhelmed. Once you gain experience and understand market preferences, you can gradually diversify your crops to increase both yield and potential profits.
Start Small, Learn, and Grow
Observe and Experiment
Starting small allows you to closely monitor your backyard farm. You can observe growth patterns, experiment with soil types, and test different irrigation methods. This hands-on learning helps you understand which crops thrive in your environment and how to optimize yields throughout seasonal cycles.
Build Confidence Gradually
By managing a smaller operation first, you gain the skills and confidence needed to expand. You’ll learn how to troubleshoot problems, maintain healthy plants or animals, and streamline daily tasks.
Scale Strategically
Once comfortable, you can gradually scale your backyard farm. Add more crops, introduce livestock, or experiment with specialty products like herbs, microgreens, or honey. Scaling thoughtfully ensures increased productivity and potential profits while keeping your farm sustainable and manageable.
📉 Avoid: Overplanting, overinvesting, or raising animals you can’t legally keep.
4. Set Up a Simple Business Plan
Even a small backyard farm thrives when you know what crops or livestock you’ll focus on. Decide whether you want to grow vegetables, herbs, fruits, raise chickens or bees, or a combination. Starting with a clear focus helps you allocate space, resources, and time efficiently.
Identify Your Customers
Understanding your audience is key to running a successful backyard farm. Decide whether your primary customers will be neighbors, farmers’ market visitors, local restaurants, or online shoppers. Each group has different preferences, expectations, and purchasing habits. For example, restaurants may value consistent supply and specialty crops, while neighbors may prefer small, convenient portions of fresh produce.
By identifying your audience early, you can tailor your crop selection, pricing, and marketing strategy to meet demand, boost sales, and ensure your backyard farming efforts are both productive and profitable.
Choose Where to Sell
Deciding where to sell your products is a critical step for a profitable backyard farm. Options include farmers’ markets, Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) programs, online marketplaces like Etsy, or a roadside stand. Each channel has unique requirements—farmers’ markets may demand weekly availability, CSAs require subscription planning, and online platforms need clear product descriptions and shipping solutions.
Your choice of sales channel can also influence what you grow or raise; for example, high-demand herbs or microgreens may sell well online, while larger produce like squash or tomatoes are ideal for markets. Planning early ensures your backyard farming operation is organized, efficient, and aligned with customer needs.
Budget for Startup Costs
A well-planned budget is essential for launching a successful backyard farm. Start by listing all potential expenses, including tools, seeds, soil, containers, fencing, animal care, and marketing efforts. Consider both one-time startup costs and ongoing maintenance expenses to get a full picture of your financial needs. Careful budgeting helps prevent unexpected costs from derailing your farm, ensures you can invest wisely in growth, and keeps your backyard farming operation financially sustainable from the very beginning.
Benefits of Goal-Setting
Setting clear, specific, and measurable goals provides your backyard farm with direction and purpose. Decide what you want to grow, how much you aim to produce, and what income or personal benefits you hope to achieve. A well-defined plan helps you track progress, adjust strategies, and make informed decisions as your farm grows. Even a modest backyard can become highly productive and profitable when guided by realistic goals. With consistent effort and planning, your backyard farming venture can be both rewarding and sustainable.
Average Startup Costs: $500–$2,000 depending on your scale and tools.
5. Learn to Grow Efficiently
Use high-yield techniques for maximum results in a small space
Square-Foot Gardening
Square-foot gardening is a highly efficient method for small backyard farms. By dividing your garden into small, manageable sections, you can grow a variety of crops without overcrowding. Each square foot is carefully planned for a specific plant, allowing you to make the most of limited space.
Efficient Crop Rotation
This method also makes crop rotation easier, helping maintain soil health and reduce pest issues. You can plan what to plant in each section seasonally, ensuring continuous productivity throughout the year.
Ideal for Beginners and Small Spaces
Square-foot gardening is perfect for beginners or anyone with limited outdoor space. It simplifies planting, watering, and harvesting, making your backyard farming experience more organized, productive, and rewarding.
Succession Planting
Succession planting is an effective way to keep your backyard farm productive from early spring through late fall. By planting new crops immediately after harvesting the previous ones, you create a continuous cycle of growth that maximizes your space and ensures a steady supply of fresh vegetables, herbs, or greens. This approach reduces gaps between harvests, minimizes wasted space, and allows you to experiment with different varieties and planting schedules. Implementing succession planting not only increases overall yield but also keeps your backyard farming efforts efficient, organized, and consistently rewarding throughout the season.
Companion Planting
Companion planting is a powerful strategy for boosting productivity in your backyard farm. By growing compatible plants together, you can naturally improve growth, enrich the soil, and repel pests without chemicals. For example, planting marigolds near tomatoes can deter nematodes, while legumes fix nitrogen to benefit neighboring crops. This method maximizes space, supports plant health, and increases overall yield, making your backyard farming more efficient and sustainable.
Drip Irrigation to Conserve Water
Using a drip irrigation system is an efficient way to water your backyard farm. It delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff while promoting deeper, healthier root growth. This targeted approach reduces water waste, prevents fungal diseases caused by overhead watering, and ensures your crops stay consistently hydrated. Drip irrigation also saves time and effort, making your backyard farming more sustainable and productive.
Composting for Free, Nutrient-Rich Soil
Composting is an excellent way to create nutrient-rich soil for your backyard farm while reducing waste. By recycling kitchen scraps, garden clippings, and other organic matter, you can naturally improve soil fertility and structure without relying on chemical fertilizers. Regularly adding compost enhances water retention, encourages healthy microbial activity, and supports stronger, more productive plants. This sustainable practice not only lowers costs but also promotes eco-friendly backyard farming year-round.
Invest in learning from local extension offices or online platforms like YouTube, Udemy, and Reddit’s r/homestead.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
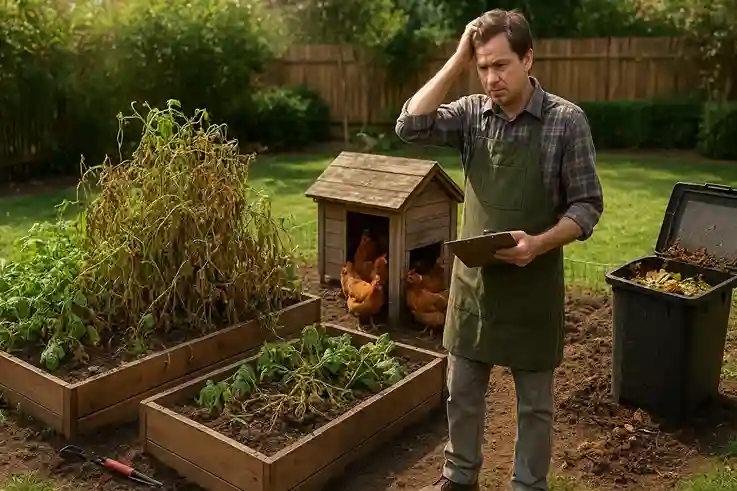

Ignoring Local Zoning Laws
One of the biggest mistakes new backyard farmers make is overlooking local zoning laws and regulations. Many cities and neighborhoods have rules about raising livestock, selling produce, or even the size and type of garden structures allowed. Ignoring these rules can result in costly fines, forced removal of crops or animals, and unnecessary setbacks. Before investing time or money, always research local ordinances and homeowners association (HOA) guidelines to ensure your backyard farm operates legally and smoothly from the start.
Planting Too Much Too Soon
A common mistake among beginners is trying to grow too many crops at once. While enthusiasm is great, overcrowding your space can quickly become overwhelming and lead to poor yields, wasted resources, and unnecessary frustration. Starting small allows you to focus on learning the basics—like soil health, irrigation, and pest control—without being stretched too thin. As you gain experience and confidence, you can gradually expand your backyard farm, ensuring steady growth and long-term success.
Not Testing the Soil First
One of the biggest mistakes new backyard farmers make is skipping soil testing. Without knowing your soil’s nutrient balance, pH level, or possible contaminants, you risk stunted plant growth and disappointing harvests. A simple soil test can reveal deficiencies and guide you on whether to add compost, lime, or other amendments. This small step saves time, money, and effort by setting the foundation for a thriving and productive backyard farm.
Forgetting to Market
Many new backyard farmers focus entirely on production and overlook the importance of marketing. Growing fresh, high-quality produce is only half the job—getting it into the hands of customers is what makes a backyard farm profitable. Whether it’s selling at farmers markets, joining CSA programs, promoting on social media, or networking with local restaurants, marketing ensures people know about your products. Without a clear strategy to reach buyers, even the best harvests can go unsold, limiting your growth and income potential.
Underpricing Your Produce or Eggs
One of the most common mistakes new backyard farmers make is setting prices too low. While it might seem like a way to attract customers, underpricing can undervalue your time, labor, and investment. It also makes it difficult to sustain your backyard farm long term.
Customers are often willing to pay a fair price for fresh, local, and homegrown products, especially when they know they are supporting sustainable practices. Research local market rates at farmers markets, grocery stores, and online platforms, then set prices that are competitive but still reflect the true value of your hard work.
For choosing the right crops, check your region’s climate. You can use the official USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map to identify what grows best in your area.
Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
You don’t need acres of land to become a farmer—just your backyard, practical knowledge, and consistent passion. A profitable backyard farm can provide more than an extra income stream. It offers fresher food, healthier living, and a stronger connection to your community. With careful planning and steady growth, even the smallest space can transform into a productive and rewarding farm.
Have you tried backyard farming or are you planning to start?
Share your experiences, challenges, and ideas in the comments—I’d love to hear your story.

Silvia Heart is a lifestyle and wellness writer with a background in apparel and a degree in fashion. She blends creativity with practical insights, guiding readers toward intentional, balanced living. Through her approachable style and thoughtful storytelling, Silvia inspires her community to embrace both everyday joy and personal growth.


