The launch of 5g network speed changed how people view mobile internet. At first, it created huge excitement. People expected instant downloads, smooth gaming, and faster streaming everywhere. However, real-world results turned out to be more mixed. In reality, 5G performance changes depending on location, device, and signal strength. Some users get speeds over 500 Mbps, while others barely notice any difference from 4G. These differences often lead to confusion and frustration. Still, 5G is an important step toward faster and smarter connectivity.
This article explains what 5G truly delivers today. You’ll learn how technology, distance, and network setup affect your actual speed. You’ll also see why 5G sometimes fails to meet the early hype. By the end, you’ll understand what makes 5G fast in some places and slower in others—and what to really expect from this evolving network.
“5G promised the future of speed — but in reality, its true power depends on where you stand and how you connect.”
What Exactly Is 5G Network Speed?

5g network speed refers to how quickly data moves between your device and the internet. It measures how fast you can download or upload files and how little delay, or latency, you experience while online. In simple terms, higher speed means smoother streaming, faster loading, and more reliable connections.
5G works by using advanced radio frequencies and wider bandwidths to carry more data at once. It also uses smarter antennas and lower latency to respond almost instantly to commands. While 4G LTE can reach up to about 100 Mbps, 5G networks can theoretically reach 10 Gbps under ideal conditions. However, most real-world speeds remain lower due to coverage, signal strength, and network demand.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Network Type | Average Download Speed | Latency (Response Time) | Theoretical Max Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4G LTE | 20–100 Mbps | 30–50 ms | ~100 Mbps |
| 5G | 200–1000 Mbps+ | 1–10 ms | ~10 Gbps |
Even with these differences, 5g network speed continues to evolve as technology and coverage improve each year.
The Factors That Influence 5G Speed
5G promises faster, smoother, and smarter connectivity. Yet, its real performance depends on several key factors. From spectrum bands to device capability, each part of the system shapes your experience with 5g network speed.
Spectrum Bands: Low, Mid, and mmWave
5G uses three main spectrum bands. Each one behaves differently.
- Low-band 5G travels the farthest. It works well in rural areas but offers speeds similar to 4G.
- Mid-band 5G strikes a balance. It covers cities well and usually reaches a few hundred megabits per second.
- mmWave 5G is the fastest, often hitting gigabit speeds. However, it works only over short distances and can’t pass through walls easily.
Moreover, most U.S. carriers rely on mid-band frequencies. These give stable speeds but not the extreme rates that mmWave promises. Therefore, your location and the spectrum in use both shape your experience.

Distance from Towers and Signal Strength
Your distance from the nearest 5G tower is another critical factor. The farther you are, the weaker the signal becomes. Strong signals allow your phone to send and receive data efficiently. Weak signals cause slower speeds and more interruptions.
Objects like walls, trees, and even weather can block 5G waves—especially mmWave. As a result, users in open areas often enjoy faster connections than those inside buildings. Moving just a few hundred feet can sometimes double or halve your internet speed.
Network Congestion and User Load
5G networks share bandwidth among many users. When too many people connect at once, speeds drop. During busy hours—such as evenings—download rates often fall noticeably. Therefore, congestion plays a large role in how fast your device performs.
Carriers are expanding capacity using advanced features like beamforming and network slicing. These tools help direct traffic efficiently and keep connections stable, even in crowded zones.
Device Capability and Software
Not all phones handle 5G equally. Older devices or cheaper models may use limited antennas or slower modems. Modern 5G phones, however, include advanced chipsets that support multiple bands and faster processing.
Moreover, software updates can improve how devices manage 5G signals. Keeping your system updated ensures your device performs at its best.
In summary, 5g network speed depends on many moving parts—spectrum choice, tower distance, network congestion, and device technology. As networks expand and devices improve, users will experience faster, more reliable 5G in more places than ever before.
Real-World 5G Performance Across the U.S.
Across the United States, 5g network speed varies widely by location. In major cities, most users see average download speeds between 200 and 500 Mbps. These numbers are far higher than 4G LTE averages, which usually stay below 100 Mbps. Moreover, in some downtown areas with mmWave coverage, 5G can reach 1 Gbps or more under ideal conditions. However, those top speeds are rare and often limited to small coverage zones.
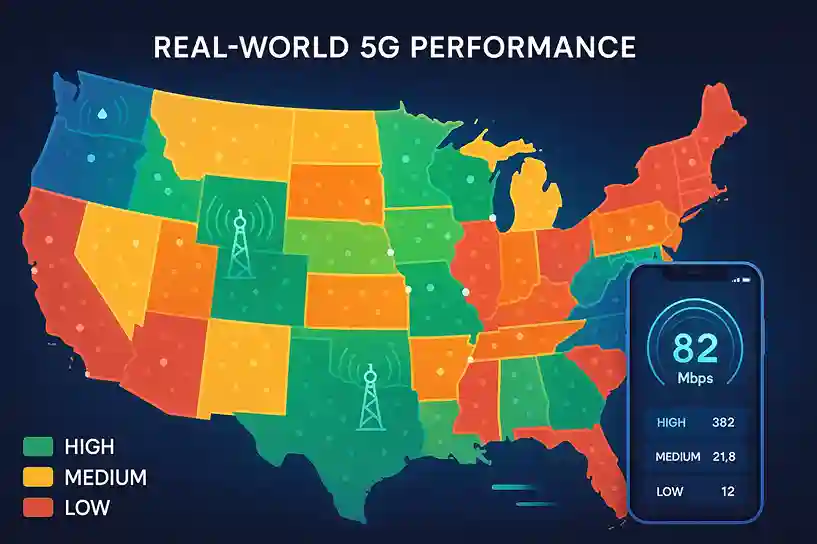
Urban vs. Rural Differences
City areas usually deliver higher 5G performance. Urban networks have more towers and stronger mid-band coverage. Therefore, people in places like New York, Chicago, and Los Angeles enjoy much faster speeds. In contrast, rural regions often use low-band 5G. As a result, speeds there tend to stay near 50 to 150 Mbps. The longer distance between towers and fewer upgrades keep rural 5G stable but slower.
Carrier Variability and Coverage
Not all carriers perform the same. Some focus on wide coverage using low-band signals. Others build mid-band systems that offer more speed but shorter range. Therefore, depending on your carrier, your 5G experience can change from one block to the next. Even in one city, performance often shifts because of tower placement or local interference.
Environmental and Real-World Effects
The environment has a strong impact on 5g network speed. Thick walls, trees, or glass can block signals easily. Even light rain or large crowds can slow performance. Moreover, when many people connect at once, the network becomes congested. As a result, speeds drop during busy hours, especially in city centers.
In short, 5g network speed across the U.S. keeps improving but remains uneven. City users often see faster, more reliable service. Rural users get broader reach but lower peak speeds. Your real results depend on your carrier, location, and surroundings—each playing a big part in how fast 5G feels every day.
Why 5G Feels Slower Than Expected
Many people expected lightning-fast connections from 5g network speed. Yet in daily use, it often feels slower than promised. The reason lies in the difference between lab results and real conditions.
Lab Tests vs. Real Life
In controlled lab tests, 5G reaches incredible speeds—sometimes over 1 Gbps. However, those tests happen under perfect settings: short distances, no obstacles, and no network traffic. In reality, your connection faces limits from the environment, signal range, and user load. Therefore, real-world performance rarely matches what advertisements show.
Limited mmWave Coverage
The fastest form of 5G, called mmWave, has very short range. It works well outdoors and near towers but struggles indoors or behind walls. Most users connect to slower mid-band or low-band networks instead. As a result, average speeds drop sharply compared to those top-tier lab speeds.
Network Sharing and Congestion
5G networks share bandwidth among many users. During busy hours, when thousands connect at once, speed drops noticeably. Streaming or gaming may lag or buffer, especially in crowded places. Moreover, some carriers still rely on mixed 4G and 5G systems. This hybrid setup limits full 5G performance.
Real Expectations
It’s normal for 5G to feel slower in certain spots. Walls, weather, and distance all interfere with signals. Even modern phones can’t always connect to the strongest frequency available. Still, 5G remains an upgrade over 4G in most cases.
In short, 5g network speed seems slower because the real world is full of challenges that lab tests don’t face. The technology keeps improving, though. With better coverage and more towers, true 5G speed will continue to grow—and users will finally feel the difference promised at launch.
The Role of Devices and Network Infrastructure
Your 5g network speed depends not only on towers but also on the device in your hand. Modern phones and the networks behind them work together to deliver fast, stable connections. When either one is outdated, performance drops.
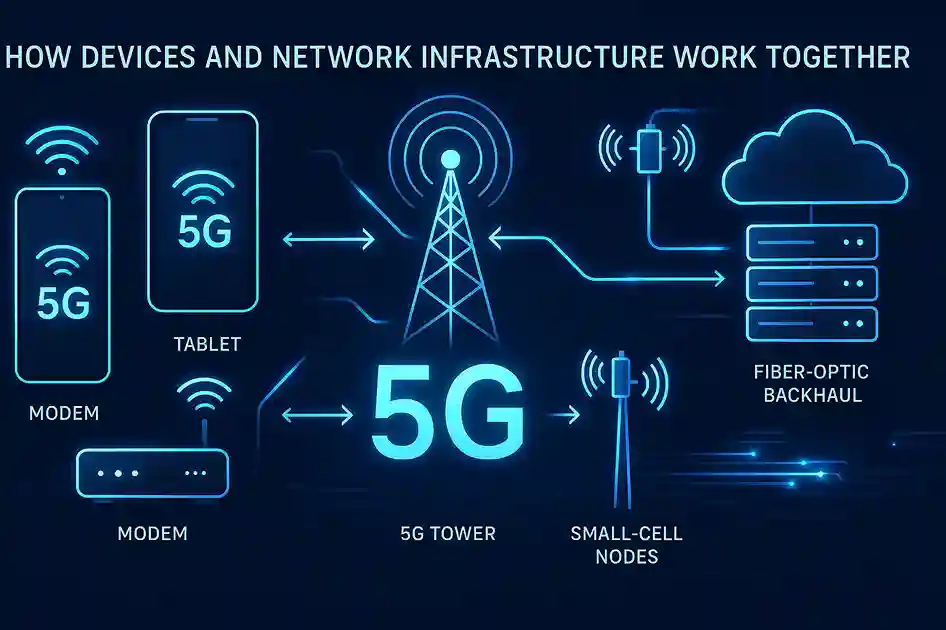
New Chipsets and Antennas
New smartphones use advanced chipsets built for 5G. These chips handle higher frequencies and process data faster. They also include multiple antennas that can connect to several bands at once. As a result, users experience smoother streaming, quicker downloads, and lower latency. Moreover, these chipsets manage battery use better, helping phones stay cooler and last longer even under heavy data loads.
Why Older Devices Fall Behind
Older phones often lack the hardware needed for full 5G support. Many can connect only to low-band signals, which provide broad coverage but slower speeds. Some can’t switch efficiently between 4G and 5G, causing connection drops or longer load times. Therefore, even in strong signal areas, older devices fail to reach the network’s true potential. Upgrading to a 5G-ready model makes a major difference in performance and stability.
The Importance of Carrier Aggregation and Small Cells
5G networks rely on new technology to deliver speed and coverage. One key feature is carrier aggregation—a method that combines multiple frequencies into one powerful signal. This boosts both download rates and reliability.
Another major upgrade comes from small cells. These are compact antennas placed on poles, buildings, and streetlights. They fill coverage gaps and improve signal strength in busy areas like downtown streets or stadiums. Moreover, small cells reduce network strain by bringing connections closer to users.
In summary, the true power of 5g network speed depends on both modern devices and an upgraded network. New chipsets unlock faster processing, while advanced infrastructure ensures those signals reach you consistently. As more cities add small cells and carriers expand mid-band coverage, everyday 5G experiences will grow faster, smoother, and far more reliable.
5G Speed vs. 4G LTE: Is the Difference Worth It?
The shift from 4G to 5G promised a revolution in connectivity. But many users still ask whether 5g network speed truly outperforms 4G in everyday use. The answer depends on where, when, and how you connect.
Speed, Latency, and Consistency
The most obvious difference between 4G and 5G is speed. 4G LTE typically delivers 20 to 100 Mbps, while 5G can reach 200 to 1000 Mbps in real-world settings. In ideal conditions, 5G can even break 1 Gbps. Latency—the delay before data starts moving—is also much lower on 5G. Average latency drops from about 40 milliseconds on 4G to under 10 milliseconds on 5G.
Yet, speed alone doesn’t tell the whole story. 4G remains more consistent, especially in rural or indoor areas. 5G performance depends heavily on coverage and frequency band. Therefore, while 5G wins in top speed, 4G still leads in reliability for now.
| Feature | 4G LTE | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Average Speed | 20–100 Mbps | 200–1000 Mbps+ |
| Latency | 30–50 ms | 1–10 ms |
| Consistency | High | Moderate (varies by band) |
| Coverage | Wide | Growing but uneven |
When 5G Truly Outperforms 4G
5G shows its real strength in crowded areas and high-demand situations. Stadiums, airports, and concerts often overload 4G networks. Yet, 5G handles large crowds better thanks to network slicing and beamforming. These technologies manage data more efficiently, reducing lag and keeping connections stable.
In smart cities, 5G supports advanced systems like real-time traffic control, connected cars, and remote monitoring. Still, for basic browsing or video streaming, 4G remains more than enough in most places..
The Future of 5G Network Speed
The future of 5g network speed looks bright. As technology advances, speeds will rise, and connections will become steadier. New systems like standalone 5G, network slicing, and edge computing are set to transform how we use mobile data.

Standalone 5G
Most 5G networks today still depend on older 4G systems. This slows performance and limits full potential. Standalone 5G removes that link completely. It uses its own modern core network, built only for 5G traffic. As a result, latency drops, and connections become more stable. Moreover, it supports new uses such as smart factories, driverless cars, and remote healthcare.
Network Slicing
Network slicing is another major upgrade. It allows one physical network to split into several virtual parts, called “slices.” Each slice serves a specific task. One may power gaming, another may handle medical devices, and another may manage emergency data. Therefore, each service gets the right speed and reliability it needs.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings data closer to users. Instead of traveling to faraway data centers, information moves through nearby servers. This cuts delay and improves response time. For everyday users, that means faster streaming, smoother video calls, and quicker app loading. Moreover, it reduces traffic on large networks by handling data locally.
Expanding Coverage and Speed
5G coverage continues to grow across the U.S. Rural regions gain more low-band towers, while cities expand with mid-band and mmWave zones. As coverage widens, average speeds will keep rising. Experts expect typical downloads to double over the next few years.
In short, 5g network speed is only getting started. Standalone networks, slicing, and edge computing will make connections faster and more dependable. The future of 5G won’t just mean speed—it will mean stronger, smarter, and more reliable communication for everyone.
Beginner Mistakes to Avoid When Testing 5G Speed
Testing 5g network speed may sound simple, but small errors can make your results inaccurate. Many users test without realizing how signal strength, location, or old tools affect their readings. Knowing what to avoid helps you measure true performance and understand your connection better.
Testing Indoors or Near Obstacles
One of the biggest mistakes is testing indoors. Thick walls, metal roofs, or even windows can block or weaken 5G signals. Trees and nearby buildings also create interference. As a result, your test may show much slower speeds than the network can deliver. For the most accurate results, test outdoors or near a clear, open area where your phone can connect directly to a tower.
Using Outdated Speed Test Apps
Another common error is using old or unreliable testing apps. Outdated tools often can’t detect new 5G features, like mid-band or mmWave performance. Therefore, results may appear lower than they should. Always use updated versions of trusted apps such as Ookla Speedtest or Fast.com. These recognize modern 5G bands and record more precise data.
Ignoring Firmware and Device Updates
Your phone’s software affects 5g network speed readings, too. Older firmware can block new improvements or slow performance. Moreover, outdated modems may not switch between 4G and 5G efficiently. Before testing, check that your phone has the latest software and carrier updates installed. This ensures you get accurate and stable readings.
Testing During Network Congestion
Speed also drops during busy hours when many people connect at once. Evening tests in crowded areas may show slower numbers, even on a strong network. Try running tests at different times of day to see the true range of your 5G speed.
Moving During the Test
Some users walk or drive while testing. Movement causes the signal to change rapidly, which skews results. Stay still during each test for the most consistent outcome.
In short, accurate 5g network speed tests require care and patience. Test outdoors, use updated tools, and keep your phone software current. Small improvements in how you test can reveal the real power of your 5G connection—and help you understand whether it’s performing as it should.
FAQs About 5G Network Speed
Conclusion
The story of 5g network speed shows steady progress, not perfection. It has changed how people connect, stream, and share data. Yet, real-world challenges remain. Speed depends on your carrier, device, and location. City users often enjoy faster results, while rural users see slower but steadier connections.
Still, every year brings clear improvements. Networks grow wider, and devices get smarter. Coverage gaps shrink with each upgrade. Moreover, new systems like standalone 5G, edge computing, and network slicing are unlocking greater potential. These upgrades bring faster speeds, lower delay, and stronger reliability.
In short, 5G is more than a faster version of 4G. It’s a foundation for the connected future. As innovation continues, 5g network speed will move from a luxury to a daily necessity. The best part is simple—this digital revolution is only getting started.
Have you tested 5g network speed in your area? Share your experience in the comments below.
Tell us how fast your connection feels, where you tested it, and what device you used. Your feedback helps others understand how 5G performs in real conditions across the U.S.

Amina Pierce is a tech-savvy blogger with a specialty in electronics, where she shares practical insights on gadgets, innovations, and the latest trends shaping our digital world. With a strong interest in how technology impacts everyday life, she breaks down complex topics into clear, easy-to-understand articles for readers of all backgrounds. While electronics is her main focus, Amina also enjoys writing on a variety of other subjects, including lifestyle, travel, and personal growth, making her content both diverse and engaging.
Outside of blogging, Amina loves tinkering with new devices, exploring smart home solutions, and capturing her experiences through travel photography. Her blend of technical knowledge and approachable style makes her a trusted source of information and inspiration.


