Quail eggs are gaining attention for their rich nutrition and delicate flavor. Once reserved for gourmet dishes, these tiny eggs now appear in health-conscious kitchens across the U.S. People praise them for their protein content, vitamins, and smooth texture. Yet, behind the excitement, confusion grows—are quail eggs truly healthier than chicken eggs, or just another trend? Their size may seem small, but their nutritional reputation feels larger than life. Some claim they boost immunity and energy instantly, while others question their cholesterol impact.
Understanding the truth matters, especially when these eggs become part of daily diets. Their appeal lies in balance—compact, nutrient-packed, and visually charming. As more Americans explore alternative proteins, quail eggs spark both curiosity and debate. Let’s uncover what makes these speckled gems stand apart, from their nutrient profile to the real science behind their health claims.
What Are Quail Eggs?

Quail eggs come from small ground-dwelling birds known as quails, members of the pheasant family. Each egg measures about one-third the size of a chicken egg, with a weight of roughly 9 to 12 grams. Their shells look distinct—creamy beige with brown speckles that make them visually appealing on any plate. Inside, the yolk appears larger in proportion to the white, giving quail eggs a richer color and creamier texture.
In flavor, quail eggs taste similar to chicken eggs but slightly more delicate and buttery. They blend easily into recipes, offering mild flavor with a luxurious touch. Many chefs prefer them for their presentation and nutritional density in smaller portions. Compared to chicken eggs, quail eggs contain slightly more iron, vitamin B12, and certain antioxidants per gram.
Their petite size packs surprising nutritional power, inviting attention from both health enthusiasts and culinary experts. Up next, let’s explore the detailed nutrient profile that makes quail eggs so remarkable for balanced, wholesome eating.
“Tiny in size but mighty in nutrients, quail eggs prove that good things truly come in small shells.”
The Nutritional Profile of Quail Eggs
Quail eggs may look small, yet their nutrition content rivals that of larger eggs. They offer a concentrated mix of proteins, vitamins, and minerals that support energy, growth, and overall wellness. Each egg delivers balanced nourishment in a compact form, making it ideal for health-conscious eaters.
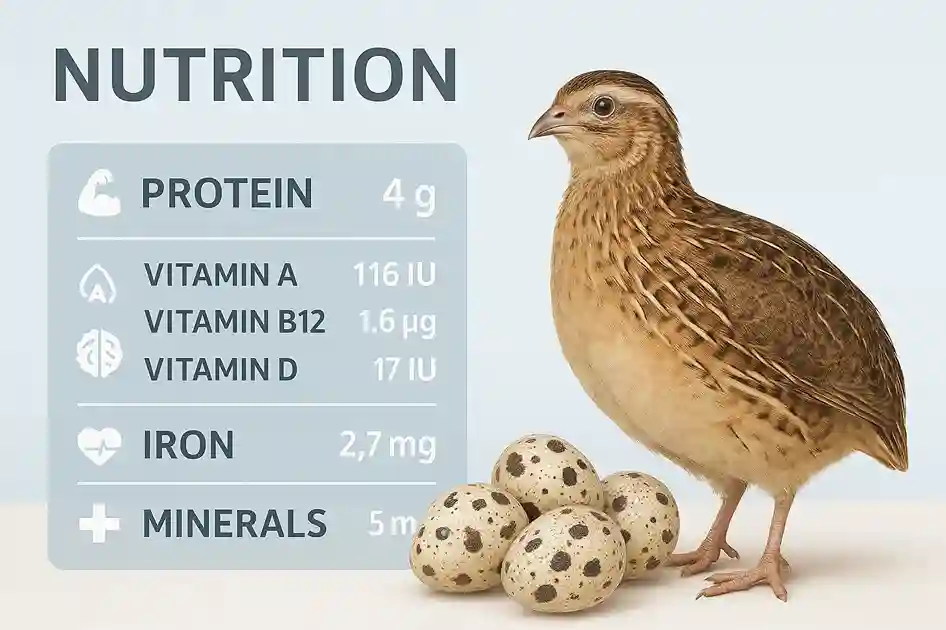
Protein Power in Every Bite
Quail eggs provide around 1.2 grams of protein per egg, a dense source for their size. Their protein carries all essential amino acids needed for muscle repair and immune function. Compared to chicken eggs, quail eggs contain more protein gram for gram, meaning you get higher nutrient efficiency in smaller servings. This makes them an excellent choice for people seeking lean, high-quality protein.
Vitamin-Rich and Energizing
These tiny eggs deliver significant amounts of vitamin A for vision and skin, and vitamin B12 for nerve health and red blood cell production. Vitamin A protects eye tissues and boosts immune defenses. Vitamin B12 helps convert food into energy and supports healthy brain function. Even small servings contribute to your daily vitamin needs.
Minerals That Matter
Each quail egg provides essential minerals like iron, zinc, and selenium.
- Iron supports oxygen transport and prevents fatigue.
- Zinc strengthens immunity and speeds wound healing.
- Selenium protects cells from oxidative stress.
In comparison, quail eggs contain more iron than chicken eggs, making them valuable for those needing extra mineral support.
Calories and Healthy Fats
One quail egg contains roughly 14 calories and 1 gram of fat, mostly unsaturated. Their yolks carry beneficial omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which aid heart health. Though small, their calorie-to-nutrient ratio makes them nutrient-dense, not energy-heavy.
Together, these nutrients create a balanced package for vitality, immunity, and metabolism. Their density supports overall wellness in small portions. Next, let’s explore how these components translate into real health benefits for the body.
Nutritional Profile of Quail Eggs (per 100g)
| Nutrient | Quail Eggs | Chicken Eggs |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 158 kcal | 148 kcal |
| Protein | 13 g | 12.6 g |
| Total Fat | 11 g | 10.6 g |
| Saturated Fat | 3.6 g | 3.1 g |
| Cholesterol | 844 mg | 372 mg |
| Vitamin A | 543 IU | 487 IU |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.6 µg | 0.9 µg |
| Iron | 3.6 mg | 1.8 mg |
| Zinc | 1.5 mg | 1.3 mg |
| Selenium | 32 µg | 31 µg |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 76 mg | 48 mg |
Note: Nutrient values are approximate and sourced from USDA FoodData Central.
Health Benefits of Quail Eggs
Quail eggs may be small, but their nutrient concentration delivers several powerful health benefits. Each serving supports vital body functions, from immunity to brain performance. Their dense combination of vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats makes them a smart addition to balanced diets.

Boosting Immunity Naturally
Quail eggs strengthen the body’s defense system through their rich content of vitamin A, zinc, and selenium. These nutrients help your immune cells function efficiently and protect against common infections. Additionally, their antioxidant properties reduce inflammation and cellular damage. Regular consumption in moderation may improve resistance to seasonal illnesses. Moreover, the protein in quail eggs supports recovery and tissue repair, both essential for maintaining strong immunity.
Supporting Brain and Eye Health
These eggs supply vitamin B12 and choline, two critical nutrients for brain and nerve function. Vitamin B12 assists in memory, mood regulation, and cognitive balance. Choline helps maintain nerve communication and supports long-term mental clarity. Furthermore, the vitamin A content promotes better vision by protecting retinal cells from oxidative stress. As a result, quail eggs contribute to sharper focus and clearer eyesight over time.
Improving Skin and Hair Quality
Quail eggs nourish the skin with vitamin A, B-complex vitamins, and selenium, which together enhance collagen production and cell renewal. Their antioxidants help reduce early signs of aging while zinc supports faster wound healing. Additionally, the fatty acids found in the yolk help maintain scalp health and prevent dryness. With consistent inclusion, these eggs may improve skin glow and hair texture naturally.
While the benefits of quail eggs are impressive, understanding their limits ensures safe use. Next, let’s address common myths and important cautions every consumer should know.
Common Myths About Quail Eggs

Despite their growing popularity, quail eggs attract many exaggerated claims that blur the line between fact and fiction. Some of these myths sound convincing, yet nutrition science paints a clearer picture of what these eggs can and cannot do.
Myth 1: Quail Eggs Cure Diseases
People often claim quail eggs can cure chronic conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease. In reality, no credible scientific study supports such curative effects. These eggs do contain nutrients that support immunity and overall wellness, but they do not replace medical treatment. Additionally, their protein and vitamin content can complement a healthy lifestyle, not act as a cure. As a result, quail eggs should be seen as nutritious food, not a natural medicine.
Myth 2: Quail Eggs Are Cholesterol-Free
Another common misconception is that quail eggs contain little or no cholesterol. However, they actually have more cholesterol per gram than chicken eggs. People believe quail eggs lower cholesterol, but studies show moderation matters more than avoidance. The key lies in balanced consumption—small portions can fit easily into a heart-healthy diet. Moreover, their fats include beneficial omega-3s, which help maintain cardiovascular balance.
Myth 3: Eating Quail Eggs Daily Is Always Safe
Some assume quail eggs are so nutrient-rich that daily, unlimited intake is fine. Yet, consuming too many can increase cholesterol levels or calorie intake. Additionally, raw or undercooked eggs may carry bacteria such as Salmonella, posing food safety risks. Therefore, responsible cooking and portion control ensure safe benefits without unwanted side effects.
Now that the myths are clear, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks and precautions before making quail eggs a regular part of your diet.
Possible Drawbacks and Precautions
Quail eggs, though nutritious, come with a few considerations that every health-conscious eater should keep in mind. Their small size hides a rich concentration of fats and cholesterol, which can be beneficial in moderation but risky in excess.

Allergy Potential
Some individuals may develop allergic reactions to quail eggs, especially those already sensitive to chicken eggs. Symptoms can include mild itching, swelling, or, in rare cases, more serious responses such as difficulty breathing. Additionally, children and people with existing food allergies should introduce quail eggs gradually under medical guidance. As a result, awareness and careful observation are key when trying them for the first time.
Cholesterol Considerations
Each quail egg contains a high cholesterol level compared to chicken eggs. While dietary cholesterol doesn’t affect everyone equally, excessive intake may raise LDL levels in some individuals. Moreover, people managing heart or metabolic conditions should limit consumption and focus on balanced portions. Eating quail eggs occasionally, rather than daily, helps maintain safe cholesterol balance.
Raw Egg Risks
Raw or lightly cooked quail eggs can harbor Salmonella bacteria, which may cause foodborne illness. Always cook eggs thoroughly to eliminate this risk. Additionally, proper refrigeration and handling prevent contamination. Clean utensils and cooking surfaces further enhance safety.
Understanding these precautions allows safe and healthy inclusion of quail eggs in your meals. Next, let’s explore simple and practical ways to add quail eggs to your diet without compromising health.
How to Add Quail Eggs to Your Diet

Quail eggs fit easily into everyday meals, offering both flavor and nutrition in small portions. Their delicate size and creamy texture make them versatile for many cooking styles. Whether you prefer simple recipes or creative plating, these eggs can elevate your dishes while keeping them healthy.
Boiled and Ready-to-Eat
Boiled quail eggs are the easiest way to enjoy their benefits. Place them in gently boiling water for about four minutes, then cool and peel carefully. Sprinkle a pinch of salt or herbs for a quick, protein-rich snack. Additionally, you can store boiled eggs in the refrigerator for two to three days for convenient meal prep.
Poached or Fried for Breakfast
Poached or sunny-side-up quail eggs add gourmet appeal to morning toast or avocado bowls. Their smaller yolks cook faster, so monitor heat closely. Cook fully. Eat safely. Moreover, pairing them with whole grains or vegetables balances fat and fiber intake.
Salads and Garnishes
Add sliced or halved boiled quail eggs to green salads for extra protein. Their speckled shells and bright yolks also make them excellent garnishes for sushi, noodles, or soups. Additionally, they complement lean meats, adding richness without heaviness.
Portion and Serving Tips
Because quail eggs are nutrient-dense, moderation remains essential. Typically, four to five quail eggs equal one large chicken egg. Use that ratio to adjust recipes or serving sizes. As a result, you get balanced nutrition without excess cholesterol or calories.
Comparing Quail Eggs with Other Types of Eggs
Understanding how quail eggs differ from other eggs helps you make smarter dietary choices. Each type—duck, turkey, ostrich, and emu—offers distinct nutritional traits, flavors, and uses. Although quail eggs are tiny, they deliver impressive nutrient density compared to their larger counterparts.
Quail Eggs vs. Duck Eggs
Quail eggs are smaller but denser in certain vitamins like vitamin B12 and iron. Duck eggs, however, contain higher fat and protein content, making them richer and creamier in taste. Additionally, duck eggs are favored in baking because their yolks create a more tender crumb. Quail eggs fit better in portion-controlled diets and are often considered more digestible for sensitive stomachs.
Quail Eggs vs. Turkey Eggs
Turkey eggs are rare and larger, with more calories and fat per serving. They taste similar to chicken eggs but with a thicker texture. In contrast, quail eggs provide a slightly milder flavor and greater nutrient concentration per gram. Moreover, quail eggs are easier to find in specialty markets, while turkey eggs remain seasonal and less common.
Quail Eggs vs. Ostrich Eggs
An ostrich egg is the giant of all eggs—equivalent to about 24 chicken eggs. It offers a strong flavor and dense nutrition but is impractical for daily use. Additionally, its high cholesterol and calorie load make it less suitable for regular meals. Quail eggs, on the other hand, provide manageable portions with the same essential nutrients in moderation.
Quail Eggs vs. Emu Eggs
Emu eggs are slightly smaller than ostrich eggs but still huge, with a dark green shell and bold flavor. Their nutrition profile is rich in protein and unsaturated fats. However, they are rarely available and mostly used in gourmet cooking. Quail eggs, by comparison, are more accessible and easier to incorporate into daily diets.
Nutritional Comparison (Approximate per 100g)
| Type of Egg | Calories | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Cholesterol (mg) | Unique Trait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quail | 158 kcal | 13.0 | 11.0 | 844 | High in iron and B12 |
| Duck | 185 kcal | 12.8 | 13.8 | 884 | Rich, creamy flavor |
| Turkey | 171 kcal | 13.7 | 11.9 | 933 | Larger, rare variety |
| Ostrich | 155 kcal | 12.2 | 10.6 | 1000+ | Very large and dense |
| Emu | 165 kcal | 13.3 | 11.5 | 870 | Deep flavor, uncommon |
Each egg type has unique advantages, yet quail eggs stand out for their accessibility, nutrient density, and portion control. Next, let’s move on to answer some frequently asked questions about how to enjoy them wisely.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Conclusion: Small Yet Mighty
The quail egg proves that true nutritional power can come in the smallest form. Packed with high-quality protein, essential vitamins, and key minerals, it supports immunity, energy, and overall wellness. Its rich content of vitamin A, B12, iron, and selenium gives the body what it needs to thrive, while its delicate flavor makes it easy to include in everyday meals.
However, balance remains essential. Despite their impressive nutrition, quail eggs contain significant cholesterol and should be eaten in moderation. Cooking them fully ensures both safety and maximum nutrient absorption. Additionally, their versatility allows countless serving options—from salads to breakfast bowls—making them both practical and enjoyable.
As more people look for nutrient-dense, natural foods, quail eggs offer a simple yet powerful choice. They deliver nourishment without excess, beauty without complexity, and value without waste.
Now that you’ve learned the real facts behind quail eggs, how do you plan to enjoy them?
Share your thoughts, favorite recipes, or experiences with quail eggs in the comments below!