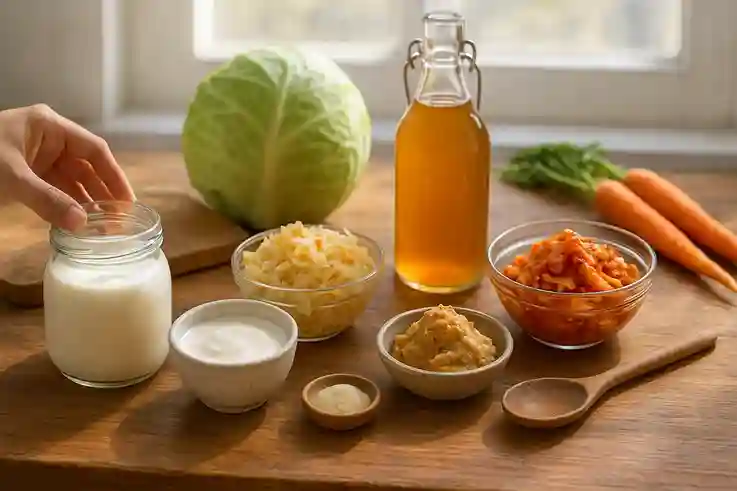
The Rising Power of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are gaining attention for their impact on health and daily energy. These foods undergo a natural process where beneficial bacteria and yeast break down sugars, creating unique flavors and enhancing nutritional value. For centuries, cultures worldwide have relied on fermentation to preserve food and improve digestion.
Today, science shows that fermented foods can do more than just extend shelf life. They help support gut health, increase energy, strengthen the immune system, and may even improve mental clarity. From yogurt and kefir to kimchi and kombucha, these foods are becoming essential parts of modern wellness.
In this blog, we’ll explore how fermented foods influence energy, digestion, immunity, and the mind, while offering practical ways to include them in your daily diet.
What Are Fermented Foods?

Fermented foods are products made through a process where natural bacteria and yeast break down sugars. This controlled breakdown, known as fermentation, enhances flavors, preserves food, and creates beneficial compounds like probiotics.
Common examples include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. Each food develops its own unique taste and nutritional profile during fermentation. Yogurt and kefir provide rich probiotics, while sauerkraut and kimchi deliver fiber and vitamins. Kombucha, a fermented tea, offers a refreshing way to support digestion.
Fermentation is not new. For thousands of years, cultures across the world have used this method to preserve food and improve health. Ancient civilizations brewed fermented beverages, created pickled vegetables, and developed dairy products that are still popular today. What began as a necessity for preservation has now become a recognized path to better wellness.
Immunity and Fermented Foods
The Gut–Immune System Connection
A significant portion of the body’s immune system resides in the gut, specifically within the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). This network interacts closely with trillions of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that naturally live in the digestive tract. Healthy gut bacteria, often called probiotics, train the immune system to recognize harmful invaders while tolerating harmless substances.
When the gut microbiome is balanced, it helps regulate inflammation, prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria, and improve the body’s response to infections. Essentially, a strong and diverse gut ecosystem acts as a frontline defense, supporting overall immunity and reducing the risk of chronic diseases linked to immune dysfunction.
How Fermented Foods Support Immunity
Fermented foods are rich in live probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that colonize the gut and support its natural functions. These probiotics help maintain a balanced microbiome, which in turn regulates immune responses. By enhancing the activity of white blood cells and other immune components, probiotics improve the body’s resilience against pathogens.
Regular consumption of fermented foods has been linked to a reduced risk of common illnesses, such as colds and digestive infections, and may even help lessen seasonal allergy symptoms. Over time, these foods can strengthen the body’s defenses, making the immune system more responsive and efficient.
Immune-Boosting Fermented Foods
Yogurt and Kefir
Are dairy-based fermented foods packed with live cultures, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species. These probiotics help replenish healthy gut bacteria, improve digestion, and support the immune system. Regular consumption can enhance the gut’s barrier function, reduce inflammation, and increase the body’s ability to fight infections. Yogurt and kefir are also rich in protein, calcium, and B vitamins, making them a nutritious addition to daily meals while promoting overall wellness.
Kimchi and Sauerkraut
are fermented vegetables rich in probiotics, which help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. They are also excellent sources of vitamins C and K, essential for immune function and blood health. Additionally, these foods contain antioxidants that combat oxidative stress, supporting overall cellular health. Regularly including kimchi or sauerkraut in your diet can improve digestion, enhance immune response, and provide a flavorful way to boost daily nutrient intake.
Kombucha
is a fermented tea rich in probiotics and organic acids, such as acetic and gluconic acids, which support gut health and digestion. The probiotics help maintain a balanced microbiome, while the acids can aid detoxification and inhibit harmful bacteria. Kombucha also contains antioxidants from tea polyphenols, which help reduce oxidative stress and support overall immune function. Regular consumption of kombucha can be a refreshing way to enhance gut health, strengthen immunity, and promote overall wellness.
Miso and Tempeh
are fermented soy products that combine high-quality protein with beneficial gut bacteria. Miso, a paste used in soups and sauces, is rich in probiotics that support digestion and immune function. Tempeh, a firm soy cake, offers a dense source of protein, vitamins, and minerals while also containing probiotics that promote a balanced gut microbiome. Including miso or tempeh in your meals can enhance nutrient absorption, support gut health, and provide sustained energy, making them excellent additions to a wellness-focused diet.
Adding these foods to meals can strengthen the body’s natural defenses in a simple, daily way.
Fermented Foods for Energy and Vitality

Probiotics and Nutrient Absorption
Probiotics found in fermented foods play a key role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. A diverse and healthy gut flora enhances the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients, such as magnesium, iron, and zinc, which are vital for energy metabolism. These minerals act as cofactors in enzymatic reactions that convert food into usable energy at the cellular level. When nutrient absorption is optimized, the body can efficiently produce ATP, the energy currency of cells, leading to sustained energy throughout the day and reduced feelings of fatigue.
Fermentation Boosts B Vitamins and Enzymes
During fermentation, beneficial bacteria synthesize essential B vitamins, including B12, B6, and folate. These vitamins play a crucial role in energy metabolism by helping convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into ATP, the body’s primary energy source. Fermented foods also contain natural enzymes that assist in breaking down macronutrients, improving digestion and nutrient absorption. Together, these vitamins and enzymes make fermented foods powerful allies in sustaining energy levels, reducing fatigue, and supporting overall vitality throughout the day.
Evidence: Reduced Fatigue with Fermented Foods
Several studies show that regular consumption of fermented foods can reduce fatigue and improve vitality. For example, individuals who included yogurt or kefir daily reported increased energy levels and better overall digestion. Fermented vegetables like kimchi and sauerkraut have also been linked to improved metabolic efficiency and sustained energy throughout the day.
Examples of Energy-Boosting Fermented Foods
Yogurt and Kefir
are dairy-based fermented foods packed with live probiotics and B vitamins. These nutrients help break down food and convert it into energy efficiently. The probiotics support a healthy gut, improving nutrient absorption, while B vitamins such as B12 and B6 play a direct role in energy metabolism. Regular consumption of yogurt or kefir can help reduce fatigue, stabilize energy levels, and provide a protein-rich boost to start the day or recover after exercise.
Kimchi and Sauerkraut
are fermented vegetables rich in probiotics, enzymes, and vitamins, including B vitamins and vitamin C. These nutrients support metabolism by aiding the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into usable energy. The probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which further enhances nutrient absorption and energy production. Regularly including kimchi or sauerkraut in your diet can improve digestion, sustain energy levels, and provide a flavorful way to support overall vitality.
Kombucha
is a fermented tea rich in probiotics and organic acids, such as acetic and gluconic acids, which support digestion and gut health. The probiotics help maintain a balanced microbiome, improving nutrient absorption and energy production. Kombucha’s organic acids may aid detoxification and stimulate metabolism, while natural antioxidants from the tea help reduce oxidative stress. Regular consumption can help reduce fatigue, improve mental alertness, and provide a refreshing way to support overall vitality throughout the day.
Miso and Tempeh
are fermented soy products that combine high-quality protein with gut-friendly probiotics and B vitamins. The protein provides long-lasting energy, while B vitamins such as B12 and folate support energy metabolism at the cellular level. Probiotics in these foods help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, improving nutrient absorption and digestive efficiency. Regular consumption of miso or tempeh can sustain energy throughout the day, support metabolic health, and add versatile, flavorful options to meals.
Fermented Oats and Sourdough Bread
are grains enhanced through natural fermentation, making them rich in probiotics and digestive enzymes. These probiotics help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, while the enzymes break down complex carbohydrates and proteins, improving nutrient absorption. Fermentation also reduces phytic acid, allowing the body to access minerals like magnesium and iron more efficiently. Regularly including fermented oats or sourdough bread in your diet can support digestion, boost energy production, and provide sustained vitality throughout the day.
Immunity and Fermented Foods

The Gut–Immune System Connection
A large portion of the body’s immune system resides in the gut, specifically within the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). This system interacts closely with trillions of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. Healthy gut bacteria, or probiotics, help the immune system distinguish between harmful and harmless substances. A balanced gut microbiome regulates inflammation, prevents overgrowth of harmful bacteria, and strengthens the body’s defense against infections and chronic disease. Essentially, a healthy gut acts as a frontline barrier for overall immunity.
How Fermented Foods Support Immune Response
Fermented foods provide live probiotics that replenish and maintain healthy gut bacteria. These probiotics enhance immune function by improving the activity of white blood cells and other immune components. Regular consumption of fermented foods has been linked to a reduced risk of common illnesses such as colds, digestive infections, and even seasonal allergies. Over time, these foods help the immune system respond faster and more efficiently to pathogens.
Immune-Boosting Fermented Foods
Yogurt and Kefir
are dairy-based fermented foods rich in live probiotic cultures, including Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species. These probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which is closely linked to immune function. By supporting healthy gut bacteria, yogurt and kefir can improve the body’s ability to fight infections, regulate inflammation, and enhance overall immune resilience. Additionally, they provide protein, calcium, and B vitamins, making them a nutrient-dense option that supports both gut and immune health daily.
Kimchi and Sauerkraut
are fermented vegetables rich in probiotics that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, a key factor in immune function. They are also packed with vitamins C and K, which support immune response and blood health, and contain antioxidants that combat oxidative stress. Regular consumption of kimchi or sauerkraut can enhance the body’s ability to fight infections, reduce inflammation, and provide essential nutrients that strengthen overall immunity while adding flavor to meals.
Kombucha
is a fermented tea packed with probiotics and organic acids, such as acetic and gluconic acids, which support gut health and digestion. The probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, improving nutrient absorption and immune function. Organic acids and antioxidants in kombucha may also reduce oxidative stress and strengthen the body’s defenses. Regular consumption of kombucha can enhance immune resilience, support digestive efficiency, and provide a refreshing way to maintain overall wellness.
Miso and Tempeh
are fermented soy products that provide high-quality protein, B vitamins, and probiotics to support gut and immune health. The protein helps maintain muscle and overall body function, while B vitamins like B12 and folate aid in energy metabolism and cellular health. Probiotics in miso and tempeh help balance the gut microbiome, improving digestion and enhancing immune response.
Including these foods in daily meals can strengthen the body’s natural defenses, support efficient nutrient absorption, and contribute to overall wellness. Regular consumption adds versatile and nutrient-dense options to a diet focused on maintaining immunity and digestive health.
Mental Health Benefits of Fermented Foods

Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
The gut and brain communicate through a network called the gut-brain axis. Healthy gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters, like serotonin and GABA, which influence mood, stress levels, and mental clarity. A balanced microbiome can help regulate this communication, supporting emotional well-being and cognitive function.
Evidence: Probiotics and Mood
Research shows that consuming probiotic-rich fermented foods may reduce stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms. Studies indicate that participants who ate yogurt, kefir, or fermented vegetables regularly reported improved mood, better focus, and enhanced mental clarity. These effects are thought to result from both improved gut health and the production of mood-regulating compounds by probiotics.
Everyday Fermented Foods for Mental Clarity
- Yogurt and Kefir: Contain probiotics that suppoFrt neurotransmitter production and gut balance.
- Kimchi and Sauerkraut: Fermented vegetables that provide both probiotics and vitamins that may aid brain health.
- Kombucha: Probiotic-rich tea that may improve focus and reduce mental fatigue.
- Miso and Tempeh: Fermented soy products supplying probiotics and B vitamins linked to cognitive function.
Including these foods in your daily diet may support a healthier gut-brain connection, reduce stress, and enhance overall mental clarity.
Common Fermented Foods and Their Key Benefits
| Fermented Food | Key Probiotics | Main Nutrients | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yogurt & Kefir | Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium | Protein, B vitamins, calcium | Gut health, immunity, energy |
| Kimchi & Sauerkraut | Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc | Vitamins C & K, antioxidants | Gut health, immunity, metabolism |
| Kombucha | Saccharomyces, Lactobacillus | Organic acids, antioxidants | Gut health, energy, immune resilience |
| Miso & Tempeh | Lactobacillus, Bacillus subtilis | Protein, B vitamins | Gut health, immunity, energy |
| Sourdough Bread & Fermented Oats | Lactobacillus | Enzymes, minerals | Digestion, nutrient absorption, energy |
Adding Fermented Foods to Your Diet

Start Small and Gradually
Begin with small servings of fermented foods to give your gut time to adjust. Start with just a few tablespoons of yogurt, kefir, or sauerkraut per day. This approach helps prevent bloating, gas, or other digestive discomfort that can occur when introducing probiotics too quickly. As your digestive system adapts, you can gradually increase portions and add a wider variety of fermented foods to your meals. Consistent, moderate intake allows your gut bacteria to thrive and ensures you gain the full benefits without discomfort.
Simple Daily Incorporation
Include fermented foods in meals you already enjoy to make them easy to maintain. Add a spoonful of yogurt to your morning smoothie or cereal, mix kimchi or sauerkraut into salads, sandwiches, or grain bowls, sip kombucha as a refreshing beverage, or stir miso into soups and sauces. Even small, simple additions throughout the day can help you consistently consume probiotics. By incorporating fermented foods naturally into your routine, you’ll support digestion, immunity, and overall wellness without drastic changes to your diet.
Store-Bought vs. Homemade Options
Both store-bought and homemade fermented foods are beneficial. Look for products labeled with “live cultures” or “probiotics” for guaranteed benefits. Homemade options, like sauerkraut or kombucha, offer flexibility and freshness, while store-bought items provide convenience and consistency.
By gradually incorporating fermented foods into your daily routine, you can enjoy their digestive, immune, and mental health benefits without discomfort.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Not Suitable for Everyone
Fermented foods may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with lactose intolerance may react to dairy-based options like yogurt and kefir, while those with histamine sensitivity could experience headaches, flushing, or digestive upset from fermented vegetables, kombucha, or aged soy products. People with certain digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may also notice increased bloating or discomfort when consuming fermented foods. It’s important to pay attention to your body’s responses, start with small servings, and adjust your intake accordingly to safely enjoy the benefits of these nutrient-rich foods.
Moderation is Key
Even for individuals without sensitivities, it’s important to consume fermented foods in moderation. Eating large portions too quickly—especially when first introducing these foods—can lead to bloating, gas, or digestive discomfort. Gradually increasing intake allows the gut microbiome to adjust to the influx of probiotics and enzymes, minimizing potential side effects. Consistent, moderate consumption helps your body reap the full benefits of fermented foods, including improved digestion, enhanced immunity, and sustained energy, without causing unnecessary strain on your digestive system.
Consult a Health Professional
If you have existing health conditions, are pregnant, or are unsure how fermented foods may affect you, consult a healthcare professional. Getting personalized advice helps you stay safe and maximize benefits.
Study Title:
Fermented Foods, Health, and the Gut Microbiome
A comprehensive review published in PubMed Central delves into how fermented foods influence the gut microbiome, emphasizing their potential to enhance digestion, immune function, and overall health.
Source: PubMed Central
FAQs
Conclusion
Fermented foods provide real benefits for energy, gut health, and immunity. Their probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, improving digestion and nutrient absorption. This, in turn, supports steady energy levels and strengthens the immune system.
Including foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, kombucha, miso, and tempeh in daily meals—even in small amounts—can make a noticeable difference over time. Start with manageable servings and gradually increase as your body adapts.
Beyond physical health, fermented foods may also support mental clarity and mood through the gut-brain connection. By making these foods a regular part of your diet, you’re investing in overall wellness.
A stronger gut may be the secret to a stronger life, unlocking energy, resilience, and a healthier, more balanced body.
We Want to Hear From You
Have you tried adding fermented foods to your diet? Share your experiences, favorite recipes, or tips in the comments below.

Ellie Clark is a passionate blogger with a specialty in education, where she shares insights on learning methods, study strategies, and ways to make knowledge more accessible. With a background in teaching and a love for lifelong learning, she brings clarity and creativity to her writing, helping readers of all ages unlock their potential. While education remains her core focus, Ellie also writes on a variety of other topics, including lifestyle, travel, and personal development, giving her blog a well-rounded appeal.
When she’s not writing, Ellie enjoys reading, exploring new cultures, and spending time in nature. Her approachable style and thoughtful advice make her a trusted voice for readers seeking both guidance and inspiration.